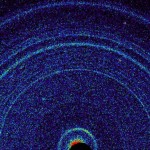
 NASA/JPL After a few dry runs, the Curiosity rover has now put its chemistry set to use at a site called the Rock Garden. For the first time, we’ve operated an X-ray diffraction system on another planet, telling us something about the structure of the minerals in the Martian soil. The first results tell us the sand the rover has driven through contains some material that wouldn’t be out of place near a volcano on Earth. Curiosity comes equipped with a scoop that lets it pick up loose soil from the Martian surface and drop it into a hatch on the main body. From there, the samples can be directed into a variety of chemistry labs. Yesterday, NASA and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory revealed the first results obtained by the Chemistry and Mineralogy (or CheMin) instrument, the first time anything of this kind has been operated on another planet. We have a lot of ways to look at the composition of the material on Mars’ surface. We can look at the absorption of light by materials (including from orbit), which can tell us a lot about its likely composition. The rover itself has a number of spectrometers, which can also tell us about the chemical composition of rocks, as well as wet and dry chemistry labs. Read 5 remaining paragraphs | Comments
NASA/JPL After a few dry runs, the Curiosity rover has now put its chemistry set to use at a site called the Rock Garden. For the first time, we’ve operated an X-ray diffraction system on another planet, telling us something about the structure of the minerals in the Martian soil. The first results tell us the sand the rover has driven through contains some material that wouldn’t be out of place near a volcano on Earth. Curiosity comes equipped with a scoop that lets it pick up loose soil from the Martian surface and drop it into a hatch on the main body. From there, the samples can be directed into a variety of chemistry labs. Yesterday, NASA and the Jet Propulsion Laboratory revealed the first results obtained by the Chemistry and Mineralogy (or CheMin) instrument, the first time anything of this kind has been operated on another planet. We have a lot of ways to look at the composition of the material on Mars’ surface. We can look at the absorption of light by materials (including from orbit), which can tell us a lot about its likely composition. The rover itself has a number of spectrometers, which can also tell us about the chemical composition of rocks, as well as wet and dry chemistry labs. Read 5 remaining paragraphs | Comments
More:
Curiosity’s first chem test: Sands of Mars taste a lot like volcano






